GATE Mechanical Engineering
Career Avenues recent GATE Mechanical ranks: 7, 21, 46, 78, 113, 118…
Our Courses

GATE Mechanical Free Trial
Start Free Trial of all Career Avenues courses. See samples of video lectures, study material and tests. And experince our award winning learning platform.
Free Trial

GATE Mechanical Engg Printed Study Material
Check Scholarship Coupon Details and Course Duration before purchase. Covers Aptitude, Maths and GATE Mechanical Engg syllabus. Includes Online Test Series, Mocks and Past GATE questions.
Starts at Rs. 7000

GATE Mechanical Engg Online Study Material
Check Scholarship Coupon Details and Course Duration before purchase. Covers Aptitude, Maths and GATE Mechanical Engg syllabus. Includes Online Test Series, Mocks and Past GATE questions.
Starts at Rs. 1000

GATE Mechanical Online Test Series
Check Scholarship Coupon Details and Course Duration before purchase. Best GATE Mechanical Engg Test Series in India. 60 Mechanical Engg, 50 Aptitude, 30 Maths Tests. 5 Mocks held in Dec and Jan.
Starts at Rs. 500

GATE Mechanical Engg Video Lectures
Check Scholarship Coupon Details and Course Duration before purchase. Detailed videos covering Aptitude, Maths and Mechanical Engg. Includes Online Test Series and Mocks.
Starts at Rs. 1000
Our Faculty
Download Our Books
You can enrol through this website or through our app using upi, wallet payments, net-banking, debit and credit cards of most banks. If you still have a difficulty, please call or whatsapp on 9930406349 and we will assist you. After enrolment, please fill enrollment form here:
Each of us requires a different kind of study program based upon our style/preference of studying. Normally, all students take our study material and test series. Many also take video lectures as it helps them clear concepts. A lot depends upon time available to prepare, current stage of preparation, etc. If you are still unsure, please contact us.
Yes, there may be few scholarships available for students from top colleges, students with good grades, students from EWS and for students whose parents are from teaching or defence services. Pls contact us on 9930406349 via whatsapp with details of course you wish to join and scholarship category needed, along with relevant documents.
As a registered Career Avenues student, you can ask your doubts here and our faculty will get back to you.
Typically 5-6 months are required, but some students need a longer time frame based on other commitments. College students start preparation 12-18 months before GATE to have more time to practise questions as they may have semester exams as well.
We suggest about 800 to 1200 hours of preparation time overall. This can be divided into 3-4 months or 12-18 months, based on your schedule.
A good score for GATE Mechanical (ME) is considered To Be: 55
Steps And Strategy To Prepare For GATE Mechanical (ME) Exam
- Take a diagnostic test – best diagnostic test is a GATE paper of any of the previous 3 years.
- Note down what you have scored and what was the actual GATE qualifying score cut-off. Note that qualification does not help you much. What you need is a good score. So note the good score mentioned above and measure the gap between your score and a good score.
- Note the GATE syllabus and mark your topics that you are good at. First try to master subjects that you are good at.
- However, some subjects like Mechanics of Materials and Thermodynamics have a high weightage. So you should definitely prepare these.
- General Aptitude does not require preparation. It requires practice. So just practice solving Aptitude questions every day for 30 minutes.
- Mathematics may have a very high weightage. But note that to get these 6-10 marks, what you have to study and practice is typically more than a core subject. So if you wish to eliminate some topics in Maths, it is fine. Master topics that you are good at.
- Take lots of section tests and Mocks. Career Avenues provides an excellent test series for GATE Mechanical (ME).
- In case you require focused GATE study material and books, you should take Career Avenues GATE Mechanical (ME) study material which has been made by IIT alumni and is focused towards GATE.
- Being a GATE aspirant, it is very important that you first know what is the syllabus for GATE Mechanical (ME) Examination before you start preparation.
- Keep handy the updated copy of GATE Mechanical (ME) Examination syllabus.
- Go through the complete and updated syllabus, highlight important subjects and topics based on Past GATE Mechanical (ME) Papers and Weightage plus your understanding of particular subject or topic.
- Keep tracking and prioritising your preparation-to-do list and the syllabus for the GATE Mechanical (ME) examination.
Section I: Engineering Mathematics
- Linear Algebra:
Matrix algebra, systems of linear equations, eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
- Calculus:
Functions of single variable, limit, continuity and differentiability, mean value theorems, indeterminate forms; evaluation of definite and improper integrals; double and triple integrals; partial derivatives, total derivative, Taylor series (in one and two variables), maxima and minima, Fourier series; gradient, divergence and curl, vector identities, directional derivatives, line, surface and volume integrals, applications of Gauss, Stokes and Greens theorems.
- Differential equations:
First order equations (linear and nonlinear); higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients; Euler-Cauchy equation; initial and boundary value problems; Laplace transforms; solutions of heat, wave and Laplace’s equations.
- Complex variables:
Analytic functions; Cauchy-Riemann equations; Cauchys integral theorem and integral formula; Taylor and Laurent series. Matrix algebra, systems of linear equations, eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
- Probability and Statistics:
Definitions of probability, sampling theorems, conditional probability; mean, median, mode and standard deviation; random variables, binomial, Poisson and normal distributions.
- Numerical Methods:
Numerical solutions of linear and non-linear algebraic equations; integration by trapezoidal and Simpsons rules; single and multi-step methods for differential equations.
Section II: Applied Mechanics and Design
- Engineering Mechanics:
Free-body diagrams and equilibrium; trusses and frames; virtual work; kinematics and dynamics of particles and of rigid bodies in plane motion; impulse and momentum (linear and angular) and energy formulations, collisions.
- Mechanics of Materials:
Stress and strain, elastic constants, Poisson’s ratio; Mohrs circle for plane stress and plane strain; thin cylinders; shear force and bending moment diagrams; bending and shear stresses; deflection of beams; torsion of circular shafts; Eulers theory of columns; energy methods; thermal stresses; strain gauges and rosettes; testing of materials with universal testing machine; testing of hardness and impact strength.
- Theory of Machines:
Displacement, velocity and acceleration analysis of plane mechanisms; dynamic analysis of linkages; cams; gears and gear trains; flywheels and governors; balancing of reciprocating and rotating masses; gyroscope.
- Vibrations:
Free and forced vibration of single degree of freedom systems, effect of damping; vibration isolation; resonance; critical speeds of shafts.
- Machine Design:
Design for static and dynamic loading; failure theories; fatigue strength and the S-N diagram; principles of the design of machine elements such as bolted, riveted and welded joints; shafts, gears, rolling and sliding contact bearings, brakes and clutches, springs.
Section III: Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences
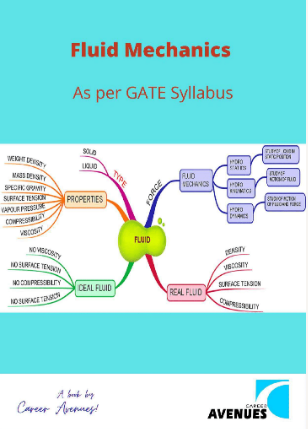
- Fluid Mechanics:
Fluid properties; fluid statics, manometry, buoyancy, forces on submerged bodies, stability of floating bodies; control-volume analysis of mass, momentum and energy; fluid acceleration; differential equations of continuity and momentum; Bernoullis equation; dimensional analysis; viscous flow of incompressible fluids, boundary layer, elementary turbulent flow, flow through pipes, head losses in pipes, bends and fittings.
- Heat-Transfer:
Modes of heat transfer; one dimensional heat conduction, resistance concept and electrical analogy, heat transfer through fins; unsteady heat conduction, lumped parameter system, Heisler’s charts; thermal boundary layer, dimensionless parameters in free and forced convective heat transfer, heat transfer correlations for flow over flat plates and through pipes, effect of turbulence; heat exchanger performance, LMTD and NTU methods; radiative heat transfer, Stefan-Boltzmann law, Wien’s displacement law, black and grey surfaces, view factors, radiation network analysis.
- Thermodynamics:
Thermodynamic systems and processes; properties of pure substances, behaviour of ideal and real gases; zeroth and first laws of thermodynamics, calculation of work and heat in various processes; second law of thermodynamics; thermodynamic property charts and tables, availability and irreversibility; thermodynamic relations.
- Applications:
Power Engineering: Air and gas compressors; vapor and gas power cycles, concepts of regeneration and reheat. I.C. Engines: Air-standard Otto, Diesel and dual cycles. Refrigeration and air-conditioning: Vapor and gas refrigeration and heat pump cycles; properties of moist air, psychrometric chart, basic psychrometric processes. Turbomachinery: Impulse and reaction principles, velocity diagrams, Pelton-wheel, Francis and Kaplan turbines.
Section IV: Materials, Manufacturing and Industrial Engineering
- Engineering Materials:
Structure and properties of engineering materials, phase diagrams, heat treatment, stress-strain diagrams for engineering materials.
- Casting, Forming and Joining Processes:
Different types of castings, design of patterns, molds and cores; solidification and cooling; riser and gating design. Plastic deformation and yield criteria; fundamentals of hot and cold working processes; load estimation for bulk (forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing) and sheet (shearing, deep drawing, bending) metal forming processes; principles of powder metallurgy. Principles of welding, brazing, soldering and adhesive bonding.
- Machining and Machine Tool Operations:
Mechanics of machining; basic machine tools; single and multi-point cutting tools, tool geometry and materials, tool life and wear; economics of machining; principles of non-traditional machining processes; principles of work holding, design of jigs and fixtures.
- Metrology and Inspection:
Limits, fits and tolerances; linear and angular measurements; comparators; gauge design; interferometry; form and finish measurement; alignment and testing methods; tolerance analysis in manufacturing and assembly.
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing:
Basic concepts of CAD/CAM and their integration tools.
- Production Planning and Control:
Forecasting models, aggregate production planning, scheduling, materials requirement planning.
- Inventory Control:
Deterministic models; safety stock inventory control systems.
- Operations Research:
Linear programming, simplex method, transportation, assignment, network flow models, simple queuing models, PERT and CPM.
Here are some recommended books for GATE Mechanical (ME) preparation:
Engineering Mechanics:
- “Engineering Mechanics” by S. Timoshenko, Sukumar Pati, D. H. Young, J.V. Rao
- “Engineering Mechanics” by S S Bhavikatti
Strength of Materials:
- “Strength of Materials” by S. S. Rattan
- “Strength of Materials” by R. K. Rajput
Theory of Machines:
- “Theory of Machines” by R. S. Khurmi
- “Theory of Machines” by S S Rattan
Fluid Mechanics:
- “A Textbook of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines” by R. K. Bansal
- “Fluid Mechanics” by Frank White
Heat Transfer:
- “Heat and Mass Transfer” by R. C. Sachdeva
- “Heat and Mass Transfer” by P. K. Nag
Thermodynamics:
- “Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach” by Yunus A. Cengel, Micheal A. Boles
- “Engineering Thermodynamics” by P. K. Nag
Manufacturing and Industrial Engineering:
- “Material Science and Metallurgy” by U. C. Jindal
- “Production Engineering” by Amitabh Ghosh
- “Industrial Engineering” by O P Khanna
Please note that while these books are recommended, you can also consider using focused GATE Mechanical (ME) study material that covers all the concepts and practice questions specifically tailored for the exam.